Introduction:
Bronchoscopy is a versatile medical procedure that plays a vital role in diagnosing and treating various respiratory conditions. This minimally invasive technique allows healthcare professionals to examine the airways and lungs, retrieve samples for analysis, and perform therapeutic interventions. As a significant tool in respiratory medicine, bronchoscopy has revolutionized the diagnosis and management of pulmonary diseases, leading to improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
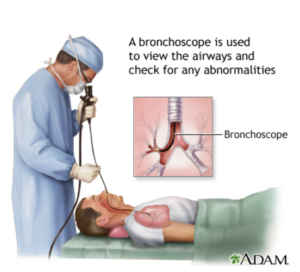
What is Bronchoscopy?
Bronchoscopy is a medical procedure that involves the insertion of a bronchoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a light and a camera, into the airways through the nose or mouth. The bronchoscope allows direct visualization of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, providing valuable insights into the condition of the respiratory system. The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia, conscious sedation, or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s needs and the complexity of the case.
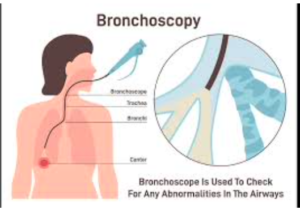
Diagnostic Applications:
Bronchoscopy serves as a diagnostic tool for a range of respiratory conditions. By visually inspecting the airways, physicians can identify abnormalities, such as tumors, strictures, or foreign bodies, that may be causing symptoms like persistent coughing, hemoptysis (coughing up blood), or difficulty breathing. Additionally, bronchoscopy enables the collection of tissue samples through biopsy, brushings, or washings, aiding in the diagnosis of lung cancer, infections, interstitial lung diseases, and other pulmonary disorders.
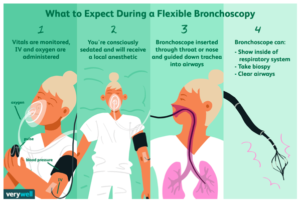
Therapeutic Applications:
In addition to its diagnostic capabilities, bronchoscopy offers various therapeutic interventions. One common procedure is endobronchial biopsy, which involves removing abnormal tissue or tumors for further examination. Bronchial stenting is another application that helps relieve airway obstructions caused by strictures or tumors, ensuring better airflow and improved breathing. Other procedures, such as balloon dilation, laser therapy, and cryotherapy, can alleviate symptoms and manage complications related to airway diseases.
Advanced Techniques in Bronchoscopy: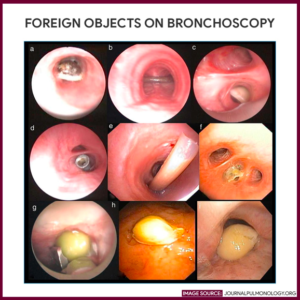 With technological advancements, bronchoscopy has evolved to encompass several advanced techniques that enhance diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy. These techniques include:
With technological advancements, bronchoscopy has evolved to encompass several advanced techniques that enhance diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy. These techniques include:
1. Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS): EBUS combines bronchoscopy with real-time ultrasound imaging to obtain detailed images of the airway walls and surrounding structures, allowing for more precise sampling of lymph nodes and tumors.
Conclusion:
Bronchoscopy has emerged as an indispensable procedure in the field of respiratory medicine, offering both diagnostic and therapeutic benefits. By providing direct visualization of the airways and facilitating tissue sampling, bronchoscopy assists in accurate diagnosis and staging of various pulmonary conditions. Moreover, with the advent of advanced techniques, physicians can target lesions more precisely and provide targeted therapeutic interventions. As technology continues to advance, bronchoscopy is poised to play an increasingly significant role in respiratory healthcare, ultimately improving patient outcomes and enhancing the overall management of pulmonary diseases.

